1- What does REST stand for?
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. (It is sometimes spelled “ReST”.) It relies on a stateless, client-server, cacheable communications protocol – and in virtually all cases, the HTTP protocol is used. REST is an architecture style for designing networked applications.
2- REST or RESTful API design (Representational State Transfer)
is designed to take advantage of existing protocols. While REST can be used over nearly any protocol, it usually takes advantage of HTTP when used for Web APIs. … REST API Design was defined by Dr. Roy Fielding in his 2000 doctorate dissertation .
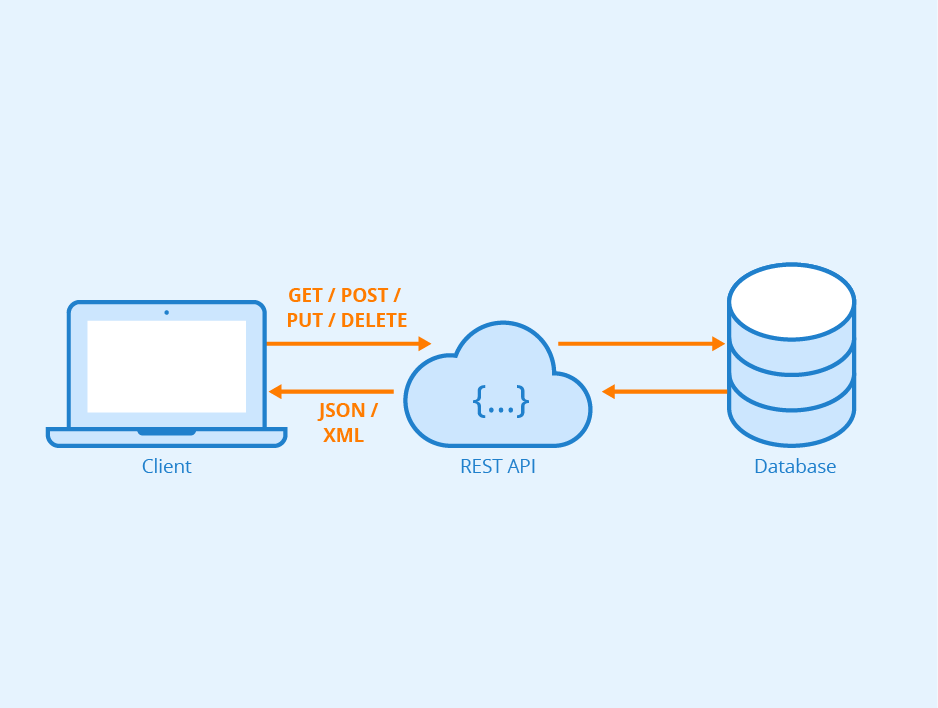
3- What is an identifer of a resource?
is a unique sequence of characters that identifies a logical or physical resource used by web technologies.
Resources whose location, grade, quality, and quantity are known or estimated from specific geologic evidence. Identified resources include economic, marginally economic, and subeconomic components.
4-What are the most common HTTP verbs?
comprise a major portion of our “uniform interface” constraint and provide us the action counterpart to the noun-based resource. The primary or most-commonly-used HTTP verbs (or methods, as they are properly called) are POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE. These correspond to create, read, update, and delete (or CRUD) operations, respectively. There are a number of other verbs, too, but are utilized less frequently. Of those less-frequent methods, OPTIONS and HEAD are used more often than others.
5-What should the URIs be based on?
URIs should be based on nouns (the resource)
URI-based standards such as Resource Description Framework make evident, resource identification need not suggest the retrieval of resource representations over the Internet, nor need they imply network-based resources at all.
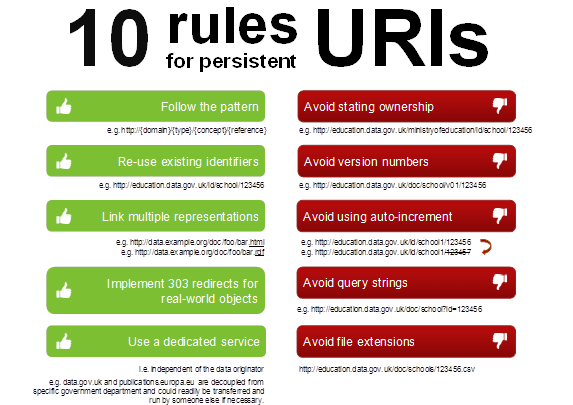
6-an example of a good URI.
https://adventure-works.com/orders
https://canvas.instructure.com/courses
7-What does it mean to have a ‘chatty’ web API? Is this a good or a bad thing?
- return simplified information and use - more fine-grained operations.
- require more calls
8-What status code does a successful GET request return?
returns HTTP status code 200 (OK).
9-What status code does an unsuccessful GET request return?
return 404 (Not Found)
10-What status code does a successful POST request return?
returns HTTP status code 201 (Created)
11-What status code does a successful DELETE request return?
returns HTTP status code 204

Ibarhem Al-omari
Email: ibrahem.omari96@gmail.com